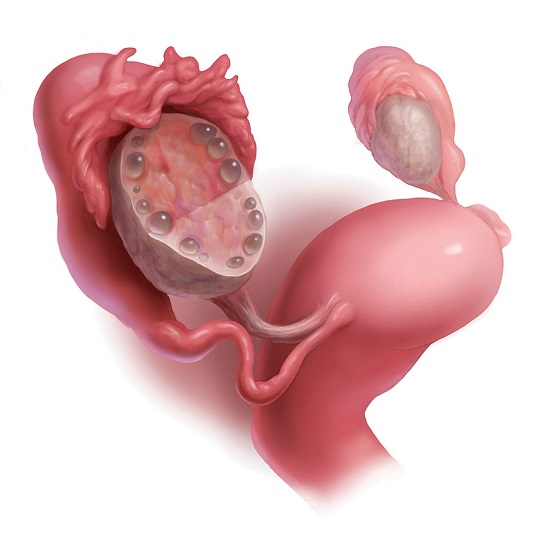
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders that women experience during their reproductive years. In this case, the woman’s ovaries become larger than normal and small cysts form inside them. These cysts can usually be the size of a pea and disrupt the normal tissue of the ovaries.
The main characteristics of PCOS include irregular menstrual cycles. Women may experience problems such as irregular menstrual periods, increased hair growth, acne, infertility, weight gain, sometimes coming at long intervals or sometimes not coming at all. In addition, the normal function of the ovaries may be disrupted, which can lead to problems with fertility. Women with PCOS do not ovulate, have increased androgen levels, and have many small cysts inside their ovaries.
Hormonal imbalances are also an important symptom of PCOS. Normal hormone levels in women may vary in women with PCOS. High levels of male sex hormones (androgens), especially testosterone, can cause symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive facial and body hair growth) and acne.
PCOS doesn’t just affect the reproductive system; it can also affect metabolic health. Metabolic issues such as insulin resistance have been associated with PCOS and can increase the risk of health problems such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
For these reasons, women with polycystic ovary syndrome should be closely monitored not only for fertility issues, but also for their effects on overall health and quality of life.
What are the symptoms of polycystic ovary?
Irregularities in the Menstrual Cycle: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome often experience irregularities in their menstrual cycles. These irregularities can be in the form of frequent periods or sometimes not having periods at all. Some women may also experience very painful periods.
Hirsutism (Excessive Hair): Women with PCOS may experience more hair than normal, especially on the face and body. This condition is especially noticeable in areas such as the chin, upper lip, chest and back. This hair may be thick and dark.
Acne: Polycystic ovary syndrome can also trigger acne. The frequency of pimples and blackheads on the face, back or chest may increase. This occurs as a result of hormonal imbalances.
Increased Insulin Resistance and Obesity: Women with PCOS often experience insulin resistance. This means that the body responds less to the hormone insulin than normal. As a result, the ability to regulate blood sugar is affected, which can increase the risk of obesity.
Difficulty in Conceiving: It may be difficult for women with PCOS to conceive naturally. Factors such as irregular ovulation and lack of ovulation can have an impact on fertility. Therefore, the effects of PCOS can be a significant concern for women planning a pregnancy.
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort: Some women may experience abdominal pain or discomfort associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. This pain is usually associated with irregular periods and is usually mild to moderate.
These are the common symptoms of PCOS, but not all women experience them to the same degree. Some women may experience symptoms that are milder, while others may have more severe symptoms. Therefore, it is important for a doctor to evaluate for diagnosis and treatment.
What are the Causes of Polycystic Ovary?
Genetic Factors: Genetic factors are thought to play a role in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. Women with a family history of PCOS or similar hormonal disorders are at higher risk of developing PCOS. This may be due to certain gene variants.
Insulin Resistance: Most women with PCOS have insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that allows blood sugar to be taken into cells. In the case of insulin resistance, the body is forced to produce more insulin than normal. This can increase testosterone production in the ovaries and affect ovulation.
Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances are evident in polycystic ovary syndrome. In particular, changes in the ratio between LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) can affect the normal ovulation process. In addition, high testosterone levels and low progesterone levels have also been associated with PCOS.
Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle factors can increase the risk of PCOS. In particular, obesity, lack of physical activity, unhealthy eating habits and stress can be effective in the development of PCOS. Obesity can exacerbate PCOS symptoms by increasing insulin resistance and can negatively impact fertility.
Each of these factors contribute to the complex etiology of PCOS. However, they can vary between individuals and may not be equally effective in every woman. Often, a combination of multiple factors can cause PCOS. Therefore, a complete understanding and identification of the factors that contribute to the development of PCOS is important in developing treatment and management strategies.
How is Polycystic Ovary Diagnosed?
Putting the Symptoms and Ultrasound Results Together: Diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome usually begins with symptoms. The doctor evaluates the patient’s symptoms such as menstrual irregularities, hirsutism, and acne. In addition, the patient’s medical history and family history are also reviewed.
Blood Tests: Blood tests play an important role in the diagnosis of PCOS. Blood tests are performed to evaluate hormonal imbalances. In particular, levels of hormones such as LH (luteinizing hormone), FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), estradiol, testosterone, and insulin are measured. These tests help identify hormone imbalances and rule out other possible causes of PCOS.
Measuring Hormone Levels: Another important test in the diagnosis of PCOS is measuring the levels of hormones related to insulin resistance and metabolic health. Insulin levels, in particular, can be evaluated with a glucose tolerance test (OGTT). This test helps determine the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Ovarian Ultrasound: The most commonly used imaging method for the diagnosis of PCOS is ovarian ultrasonography. This test is used to evaluate the size, shape, and cysts inside the ovaries. In women with PCOS, the ovaries are usually large and have one or more cysts inside them. However, these cysts are not necessarily present and are not sufficient on their own to diagnose PCOS.
The results of all these tests are evaluated together to diagnose PCOS. However, diagnosing PCOS can be complex and can sometimes require several visits and tests. Once a diagnosis is made, a treatment and management plan can be created.
What Should Those With Polycystic Ovary Do?
Adopting a Healthy Diet:
People with PCOS should adopt a balanced and healthy diet. This should include low glycemic index foods, whole grains, vegetables, fruits, protein sources, and healthy fats.
A good diet can help keep insulin levels balanced and help control weight.
Weight Control:
Weight control is important for individuals with PCOS. Obesity can aggravate PCOS symptoms and have negative health effects.
Weight loss, combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise, can reduce insulin resistance and correct hormonal imbalances.
Exercising Regularly:
Exercise is important for relieving PCOS symptoms and improving overall health.
Getting at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week can reduce insulin resistance and support weight control.
Strength training can also increase muscle mass and boost metabolism.
Avoiding Stress:
Stress can increase PCOS symptoms and trigger hormonal imbalances.
Avoiding stress or using stress management techniques is important for individuals with PCOS. Stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and hobbies can be helpful.
Regularly Using Medications Recommended by the Doctor:
It is important to use medications used in the treatment of PCOS regularly. Regular use of treatments such as hormonal balancing drugs, insulin sensitivity-enhancing drugs, or ovulation induction drugs is especially important.
Being meticulous about the dosage and timing recommended by the doctor can increase the effectiveness of the treatment.
Going to Regular Follow-up Exams:
Individuals with PCOS should go to their doctor regularly. These check-ups are important for monitoring symptoms, evaluating treatment, and updating the treatment plan if necessary.
Those with polycystic ovary syndrome can relieve symptoms and improve their overall health by implementing these healthy lifestyle changes. However, it is important to talk to their doctor about any treatment or lifestyle changes.
How is Polycystic Ovary Treated?
Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pills):
Oral contraceptives are a frequently used treatment option to relieve symptoms of PCOS. These medications can improve menstrual cycles, reduce hirsutism, and control acne.
Additionally, birth control pills can improve fertility by regulating ovulation and reduce the risk of endometrial cancer.
Medications that Increase Insulin Sensitivity:
Medications that reduce insulin resistance can help regulate insulin levels and improve hormonal imbalances in individuals with PCOS. Medications such as metformin can reduce insulin resistance and improve glucose tolerance.
Medications that increase insulin sensitivity are often recommended for obese or insulin-resistant PCOS patients.
Ovulation Induction:
Ovulation induction therapy may be considered for women with PCOS who want to get pregnant. This treatment involves medications or hormone injections used to regulate ovulation.
Ovulation induction is used to increase fertility and promote pregnancy. However, this treatment should be monitored by a doctor who prescribes it.
Surgical Treatment Options:
There are also surgical options to treat certain conditions caused by PCOS. For example, surgical procedures such as electrolysis or laser hair removal may be considered for excessive hair growth.
Lifestyle Changes and Diet:
Healthy lifestyle changes play an important role in managing the symptoms of PCOS. Factors such as adopting a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, avoiding stress, and not smoking can help relieve symptoms and improve overall health.
Treatment often depends on an individual’s symptoms and desire to conceive. Therefore, the treatment plan is customized for each individual and determined by Assoc. Prof. Dr. Esra ÖZBAŞLI.