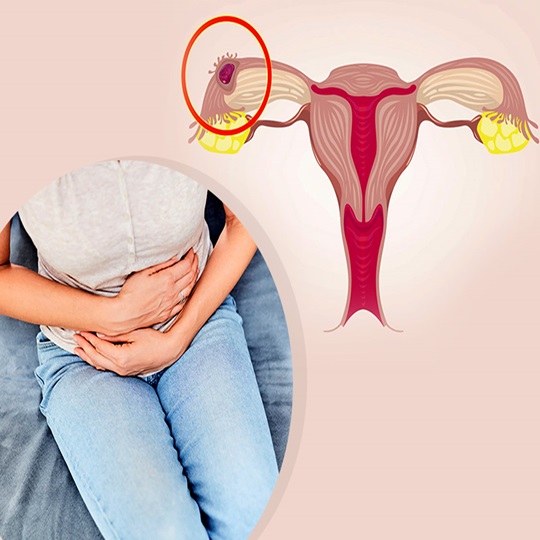
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy | An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg develops outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. Since this occurs outside of the intrauterine conditions necessary for the normal progression of pregnancy, it can cause serious medical complications such as rupture of the tubes and internal bleeding in the following weeks because there is not enough space for the pregnancy to develop.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Ectopic pregnancy occurs in approximately 1% of pregnancies. Risk factors include age, history of previous pregnancies, damage to the tubes, infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease, smoking, and certain medical conditions. The frequency of ectopic pregnancy has been increasing in recent years with the increase in assisted reproductive techniques. The reasons for this increase include hormonal changes, tubal ligation (tying of the tubes), and increased risk of infection.
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
Significant Symptoms
The specific symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are usually similar to those of a typical pregnancy. These symptoms include delayed menstruation, nausea, breast tenderness, and frequent urination. However, since an ectopic pregnancy is outside the uterus instead of inside the uterus, symptoms such as pelvic pain and bleeding may also occur in addition to typical pregnancy symptoms. Spotting-like bleeding can often be observed in ectopic pregnancy.
Some symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may be milder and less pronounced, which can make diagnosis difficult. In particular, mild pelvic pain can be confused with low-grade vaginal bleeding or symptoms of an intrauterine pregnancy. Therefore, in some cases, a detailed medical evaluation and imaging may be required to diagnose an ectopic pregnancy.
The classic triad of an ectopic pregnancy is abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and the absence of menstruation. It is very important to exclude an ectopic pregnancy in the first place in a woman presenting with these complaints. Although this triad can be observed in healthy pregnancies and in the risk of early miscarriage, it is important to exclude an ectopic pregnancy in the first step because it carries a life-threatening risk.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Clinical Examination and Medical Imaging Methods
Ectopic pregnancy is usually diagnosed using a series of clinical examinations and medical imaging methods. During the doctor’s examination, tenderness and pain in the pelvic region are examined. Ultrasonography is the most commonly used imaging method in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy can be detected by examining the ovaries and fallopian tubes in detail with ultrasonography.
When the beta hCG value in the blood is above 1000-1500 µ/L with transvaginal ultrasound, or above 5000-6000 µ/L with transabdominal ultrasound, the sac is expected to be seen in the uterus. If it cannot be seen, close monitoring is important for ectopic pregnancy.
Blood Tests and Hormonal Markers
Blood tests and hormonal markers also play an important role in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Regular measurement of beta-HCG levels, known as the pregnancy hormone, can be helpful in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. In a normal pregnancy, beta-HCG levels increase at a certain rate, whereas in an ectopic pregnancy this increase is typically slower or not at the expected rate. Progesterone levels may also be tested, as low progesterone levels can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Medical Approaches and Drug Therapy
Ectopic pregnancy treatment is performed with various methods in order to terminate the pregnancy in a healthy way and to protect the health of the mother-to-be. Medical approaches are generally used to terminate the pregnancy and remove the ectopic pregnancy material from the body. Drugs such as methotrexate can be effective in the treatment of ectopic pregnancy by preventing cell division and ensuring the absorption of the ectopic pregnancy material.
Surgical Interventions and Laparoscopic Interventions
Surgical interventions are a frequently preferred method in the treatment of ectopic pregnancy, especially in cases where the ectopic pregnancy does not respond to medical treatments or when urgent intervention is required. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical method performed through small incisions. In this method, the fallopian tubes or ectopic pregnancy material can be surgically removed. When performed at the right time and by an experienced gynecologist, laparoscopic surgery can be an effective and reliable option in the treatment of ectopic pregnancy. This method can result in minimal complications and a short recovery period, which can increase the quality of life of patients. In addition, if the surgery is performed correctly, it does not prevent the patient from having a healthy next pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy treatment should be planned individually for each patient and the treatment selection should be made by taking into account the patient’s condition, the progress of the pregnancy and other factors. During the treatment process, the patient and their family should work closely with their doctors and be informed about treatment options.
Complications and Prognosis
Ectopic pregnancy is a potentially dangerous condition that can lead to serious complications. Without early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, an ectopic pregnancy can put the mother’s health at risk. Delayed or incorrect treatment can lead to damage to the fallopian tubes, internal bleeding, and even death. However, with early diagnosis and effective treatment, most cases of ectopic pregnancy can be successfully managed and the mother’s health can be protected.
Preventive Approaches and Health Recommendations
Measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy include regular pregnancy follow-up, avoiding sexually transmitted infections, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. When planning a pregnancy, it is important to consult Assoc. Prof. Dr. Esra ÖZBAŞLI and have the necessary medical check-ups. In addition, women who have had an ectopic pregnancy in the past should be followed more carefully for future pregnancies.